Genomics Data Standardization with FHIR
Translational medicine and precision medicine involve combining clinical and genomic data to derive actionable insights that can be applied at the point of care. Typically, clinical and genomics data come from different sources: clinical data come from systems like electronic health records, laboratory information systems, and other specialty clinical systems, while genomics data are often sourced directly from the bioinformatics data pipelines responsible for processing source data from DNA sequencing machines.
Developing combined clinical+genomics datasets is currently challenging because there are not widely adopted exchange standards that cover both clinical and genomic data. In their absence, bespoke structural and semantic mappings may be used, which limits reuse and scaling. This is also complicated by the “big data” challenges associated with genomic data due to its breadth and depth: a single human genome ranges from hundreds of megabytes to gigabytes in size, which is larger than most clinical datasets for all patients in a study.
1 Why FHIR for genomics standardization?
FHIR provides a cohesive framework for developing a standardized genomic learning health system. It proposes extensible and modular information models, operations, and tooling needed for the exchange and processing of clinical and genomic data.
The HL7 genomics community aspires to address the entire clinical genomics data flow, from ordering to results reporting to evidence generation. This is possible because of the breadth of the HL7 community which has dedicated and collaborative working groups that address each part of the flow.
3 Relevant FHIR Tools
3.1 VCF to FHIR
vcf2fhir is a utility which converts VCF files into HL7 FHIR format, conforming to the HL7 FHIR GRIG. It is open-sourced and available on GitHub.
4 Engaging with the FHIR genomics community
4.1 HL7 Clinical Genomics Working Group
The HL7 Clinical Genomics Workgroup (CGWG) comprise of a diverse community of researchers, providers, and non-profit specialty organizations primarily focused standards development that supports the semantically meaningful exchange of data between parties interested in clinical, personal, and population genomic information and family health history.
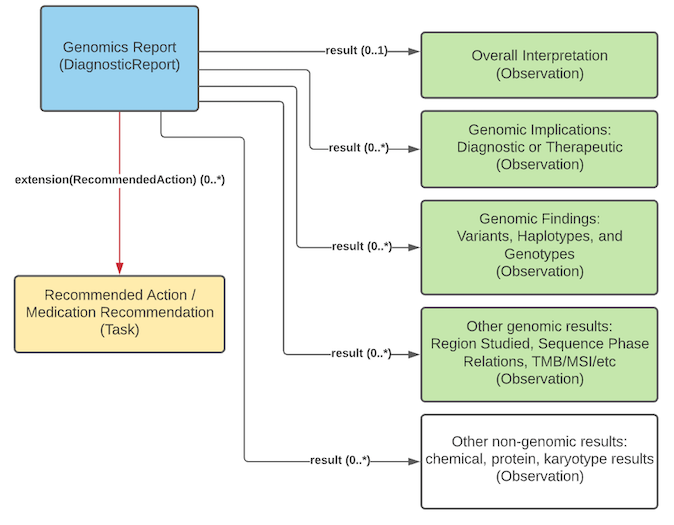
CGWG is is the author and steward of the FHIR Genomics Reporting Implementation Guide (discussed above), a FHIR-based specification for the exchange of genomics reporting elements.
4.2 CodeX FHIR Accelerator domain: GenomeX
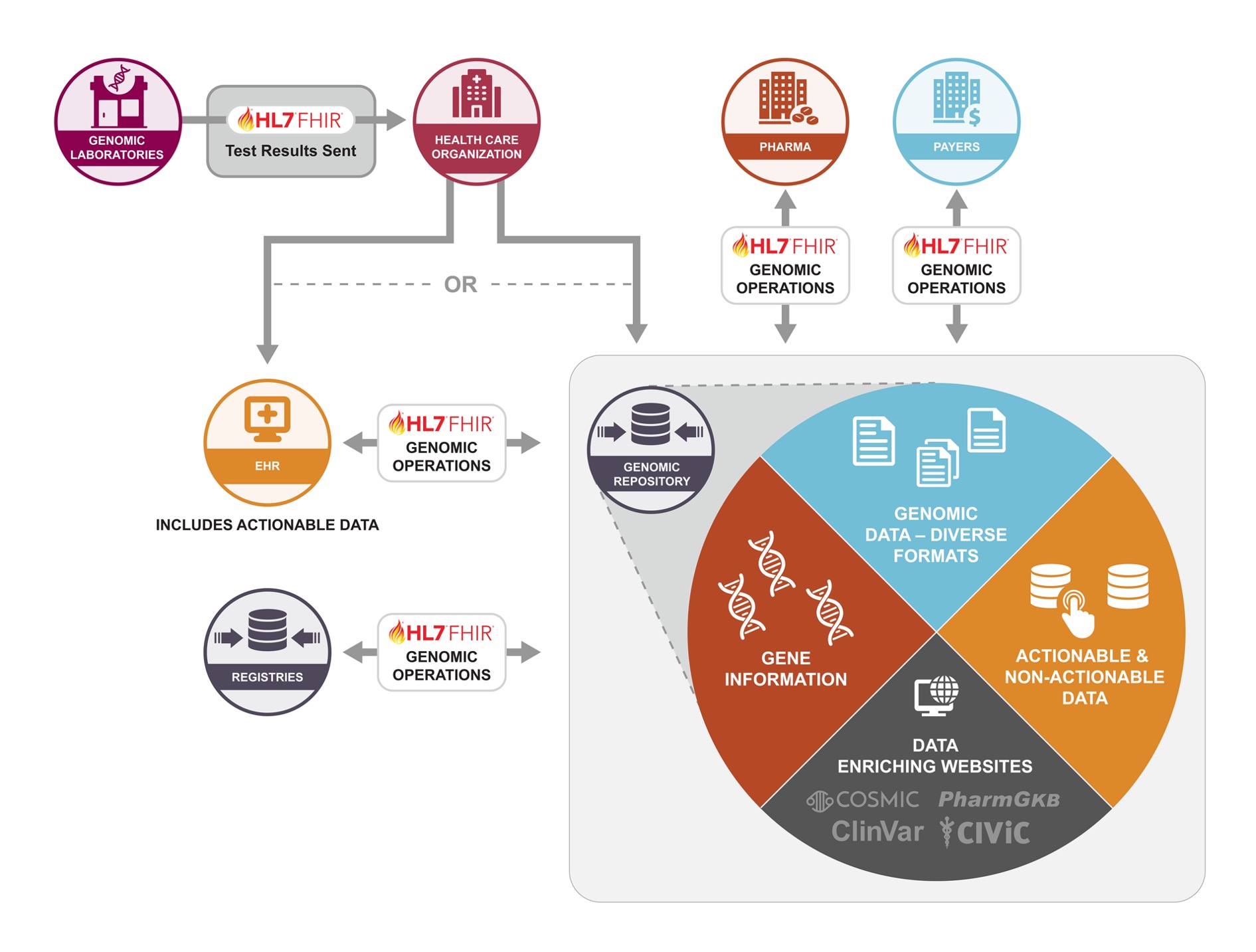
GenomeX is a domain use case under the HL7 CodeX FHIR Accelerator. GenomeX consists of a multi-stakeholder community, working together as subject matter experts, to enable high-quality, computable data for the genomics ecosystem. The community aims to ensure that the genomics FHIR-based specifications meet the needs of stakeholders as validated through real-world pilots in designated use cases.
The multi-stakeholder community represents a broad spectrum involved in genomic message and data exchange with representatives that include genomic reference labs, EHR vendors, provider organizations, life sciences, analytic and decision support platforms, and non-profit organizations and consortiums.
Through consensus, GenomeX stakeholders bring a real-world implementation focus in two use cases identified in the development of an integrated and standardized genomics solution in two major areas:
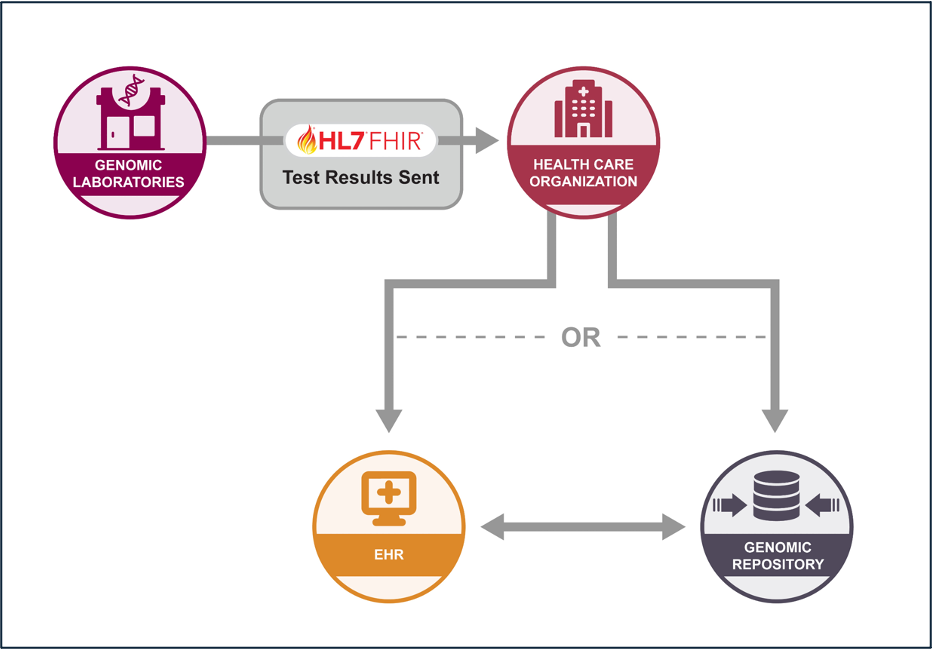
Standardizing the data exchange of genomic reports from a reference lab to a clinical application.
Standardizing the message exchange and access of genomic data between a genomic repository and consuming applications through FHIR-based operations.
The GenomeX community works closely with the HL7 CGWG as a validator and influencer of the existing FHIR specifications through real-world implementations.