Deployment Using Docker-Compose
1/15/25About 2 min
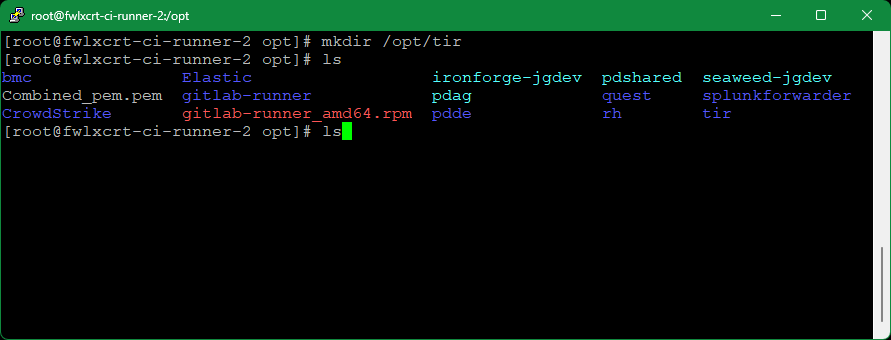
- On the target host system, create a target deployment folder (i.e. /opt/tir).
$ mkdir /opt/tir
- Copy over the latest bootstrap script from the pipeline job artifacts. This script is built in the pre-deploy stage of the current TIR gitlab pipeline and can be found in the “Prepare docker-compose” job artifacts (i.e. https://gitlab.us.lmco.com/e348832/tir/-/jobs/125468922/artifacts/browse).
It is important to use the job artifact script as it compiles text from the other run-time scripts necessary for the TIR deployment.
Generate the supporting files.
a. Move the bootstrap_tir.sh file into the target deployment folder.
b. Set the bootstrap_tir.sh mode to executable
$ chmod +x /opt/tir/bootstrap_tir.shc. From the deployment folder as the working directory, run the executable
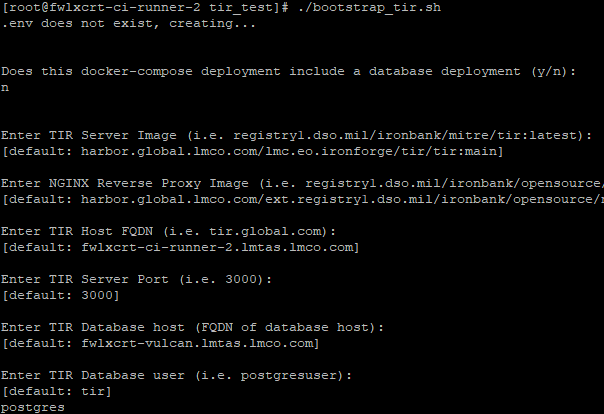
> $ ./bootstrap_tir.shd. Follow the instructions in the bootstrap to generate the supporting files
i. It will ask if a database is being deployed and then will provide questions with example answers as well as default values if no prompt is given
ii. Tips:
1. Images: Use images from public/private repos that match images listed in the default example, the hosting registry may differ but the image:tag should be similar (i.e.
your.private.registry/project/tir:v1.0.1 matches our.private.registry/our_project/tir:v1.0.1).
2. SQLITE (optional): should be true if using sqlite instead of another SQL db instance – only visible when deploying a database
3. USE_CUSTOM_REPO: This deployment allows for the nginx reverse proxy to restart upon receiving updated and valid SSL host certificates. It thus requires installation of the following packages: (openssl inotify-tools procps-ng psmisc). OpenSSL validates the certificates, inotify-tools allows for monitoring of the staged-certificate shared volume, and Procps-ng/psmisc allow the image to search for the running inotify process, and stop it, thus restarting the reverse proxy. **Set this variable to true if your server requires a private yum repository**.
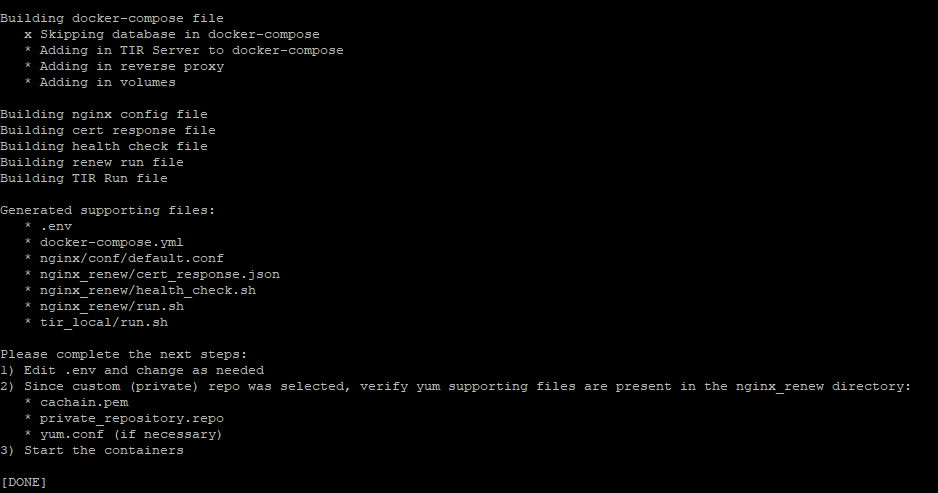
iii. At the end of the setup, the bootstrap script will display a massage stating which files had been created based on the selections in the prompts. Note the next steps listed at the bottom.
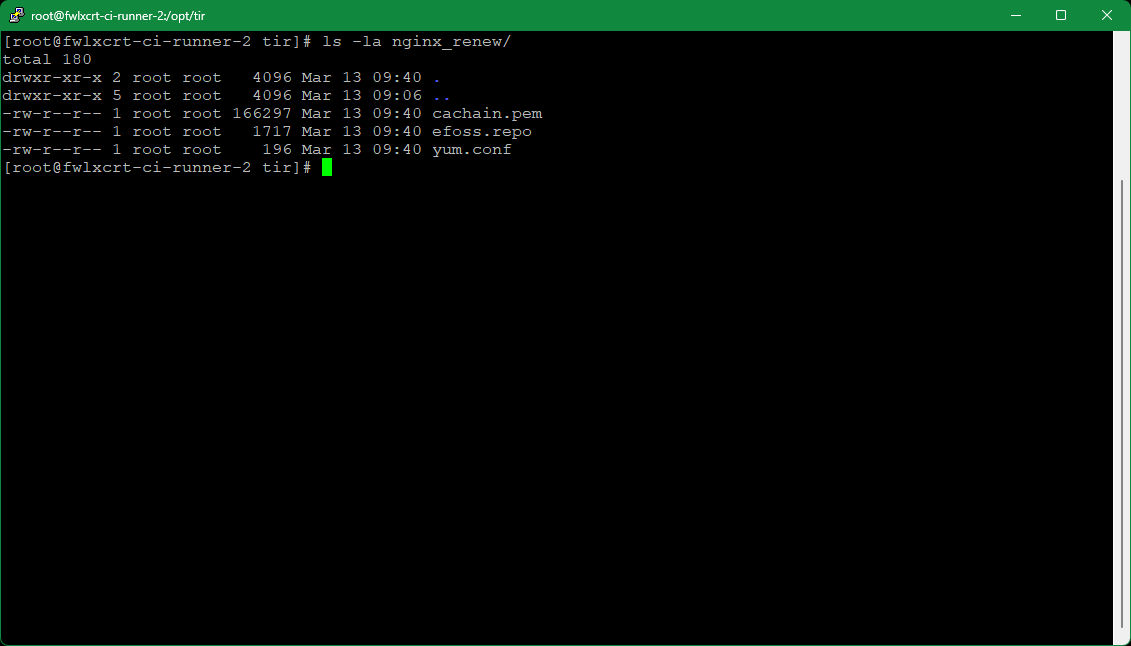
e. *If the server is using a private yum repository*, copy the following into the target deployment's nginx_renew folder from the matching tir repository’s deployment folder:
i. A cachain cert (.pem file) for ca-trust
(For LM instances)
$ curl http://crl.external.lmco.com/trust/pem/combined/Combined_pem.pem -o nginx_renew/cachain.pemf. .repo file(s) to be used from where openssl, inotify-tools, procps-ng, psmisc can be installed.
(For LM instances)
$ sed -i "s/#INSERTTOKEN#/$EFOSS\_TOKEN/g" nginx\_renew/efoss.repo && \\
$ sed -i "s/#INSERTUSERNAME#/$EFOSS\_USER/g" nginx\_renew/efoss.repog. A yum.conf file if necessary
Install docker-compose, see https://cctdocs.pages.gitlab.us.lmco.com/ironforge/hosting/deployment/index.html and perform
a. Preparation
b. docker-compose
c. Netavark network_backend install/configUse docker-compose to bring up the deployment
a. From your working directory bring up the environment with
$ docker-compose up -d
b. To see logs on your compose up use (use -f to follow)
$ docker-compose logs -f
c. To bring down the deployment, run the following:
$ docker-compose downd. Remove the volumes created by running
$ podman volume ls # shows a list of created podman volumes
> $ podman volume rm tir-... # Only use for volumes created by this docker-compose