3. Practice the Fundamentals
Revisiting the NGINX Web Server InSpec Profile
In the beginner class, we wrote and ran an InSpec profile against a test container. We then generated a report on our results and loaded them into Heimdall for analysis. Let's recap this process with some practice.
The Target
InSpec is a framework which is used to validate the security configuration of a certain target. In this case, we are interested in validating that an NGINX server complies with our requirements.
First let's find our nginx container id using the docker ps command:
docker ps
Which will return something like:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
8bs80z6b5n9s redhat/ubi8 "/bin/bash" 2 weeks ago Up 1 hour redhat8
8ba6b8av5n7s nginx:latest "/docker.…" 2 weeks ago Up 1 hour 80/tcp nginx
We can then use the container name of our nginx container nginx to target the inspec validation scans at that container.
The Requirements
InSpec profiles are a set of automated tests that relate back to a security requirements benchmark, so the controls are always motivated by the requirements.
Review
- NGINX version 1.10.3 or later.
- The following NGINX modules should be installed:
http_sslstream_sslmail_ssl
- The NGINX configuration file -
/etc/nginx/nginx.conf- should exist as a file. - The NGINX configuration file should:
- be owned by the
rootuser and group. - not be readable, writeable, or executable by others.
- be owned by the
- The NGINX shell access should be restricted to admin users.
The Controls
InSpec profiles consist of automated tests, that align to security requirements, written in ruby files inside the controls directory.
Review
If you don't have my_nginx profile, run the following command to initialize your InSpec profile.
inspec init profile my_nginx
Append the inputs sections in your profile at my_nginx/inspec.yml
name: my_nginx
title: InSpec Profile
maintainer: The Authors
copyright: The Authors
copyright_email: you@example.com
license: Apache-2.0
summary: An InSpec Compliance Profile
version: 0.1.0
supports:
platform: os
inputs:
- name: nginx_version
type: String
value: 1.10.3
- name: nginx_modules
type: Array
value:
- http_ssl
- stream_ssl
- mail_ssl
- name: admin_users
type: Array
value:
- admin
Create an inputs file in your profile at inputs-linux.yml
admin_users:
- admin
- root
Paste the following controls in your profile at my_nginx/controls/example.rb
control 'nginx-version' do
impact 1.0
title 'NGINX version'
desc 'The required version of NGINX should be installed.'
describe nginx do
its('version') { should cmp >= input('nginx_version') }
end
end
control 'nginx-modules' do
impact 1.0
title 'NGINX modules'
desc 'The required NGINX modules should be installed.'
required_modules = input('nginx_modules')
describe nginx do
required_modules.each do |required_module|
its('modules') { should include required_module }
end
end
end
control 'nginx-conf-file' do
impact 1.0
title 'NGINX configuration file'
desc 'The NGINX config file should exist.'
describe file('/etc/nginx/nginx.conf') do
it { should be_file }
end
end
control 'nginx-conf-perms' do
impact 1.0
title 'NGINX configuration permissions'
desc 'The NGINX config file should owned by root, be writable only by owner, and not writeable or and readable by others.'
describe file('/etc/nginx/nginx.conf') do
it { should be_owned_by 'root' }
it { should be_grouped_into 'root' }
it { should_not be_readable.by('others') }
it { should_not be_writable.by('others') }
it { should_not be_executable.by('others') }
end
end
control 'nginx-shell-access' do
impact 1.0
title 'NGINX shell access'
desc 'The NGINX shell access should be restricted to admin users.'
non_admin_users = users.shells(/bash/).usernames
describe "Shell access for non-admin users" do
it "should be removed." do
failure_message = "These non-admin should not have shell access: #{non_admin_users.join(", ")}"
expect(non_admin_users).to be_in(input('admin_users')), failure_message
end
end
end
Running the Controls
To run inspec exec on the target, ensure that you are in the directory that has my_nginx profile.
inspec exec my_nginx -t docker://nginx --input-file inputs-linux.yml
Profile: InSpec Profile (my_nginx)
Version: 0.1.0
Target: docker://DOCKER_CONTAINER_ID
Target ID: TARGET_ID
✔ nginx-version: NGINX version
✔ Nginx Environment version is expected to cmp >= "1.10.3"
✔ nginx-modules: NGINX modules
✔ Nginx Environment modules is expected to include "http_ssl"
✔ Nginx Environment modules is expected to include "stream_ssl"
✔ Nginx Environment modules is expected to include "mail_ssl"
✔ nginx-conf-file: NGINX configuration file
✔ File /etc/nginx/nginx.conf is expected to be file
× nginx-conf-perms: NGINX configuration permissions (1 failed)
✔ File /etc/nginx/nginx.conf is expected to be owned by "root"
✔ File /etc/nginx/nginx.conf is expected to be grouped into "root"
× File /etc/nginx/nginx.conf is expected not to be readable by others
expected File /etc/nginx/nginx.conf not to be readable by others
✔ File /etc/nginx/nginx.conf is expected not to be writable by others
✔ File /etc/nginx/nginx.conf is expected not to be executable by others
✔ nginx-shell-access: NGINX shell access
✔ Shell access for non-admin users should be removed.
Profile Summary: 4 successful controls, 1 control failure, 0 controls skipped
Test Summary: 10 successful, 1 failure, 0 skipped
Reporting Results
In the beginner class, we mentioned that you can specify an InSpec reporter to indicate the format in which you desire the results. If you want to read the results on the command line as well as save them in a JSON file, you can run this command.
inspec exec my_nginx -t docker://nginx --input-file inputs-linux.yml --reporter cli json:my_nginx_results.json
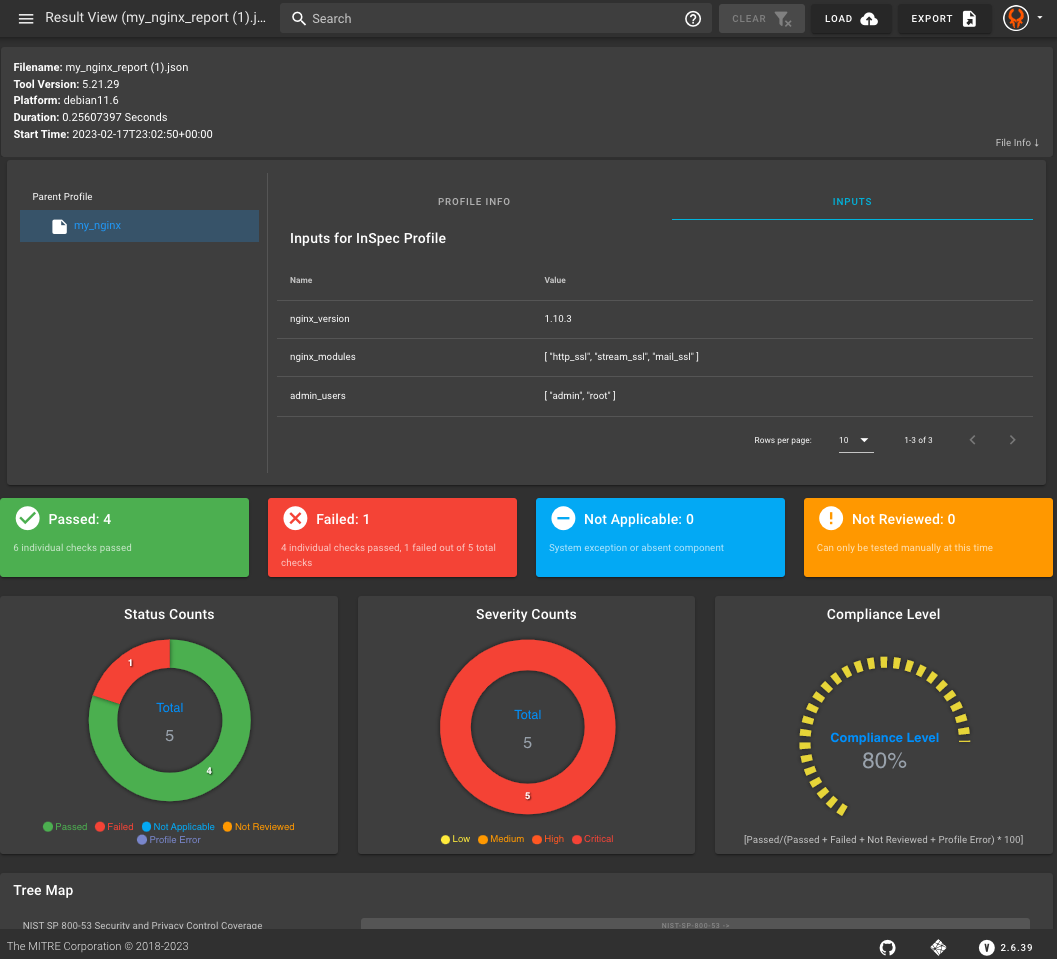
Visualizing Results
You can use this output file to upload and visualize your results in Heimdall .